

The overall change in enthalpy of dissolution of ionic compounds accounts for the change in enthalpy of each of the three steps of dissolution: separation of solvent molecules, dissociation of ionic lattice structure and hydration of free ions.Greater the attraction, higher the solubility as hydration of ions occurs more readily. The forces of attraction between the particles of solid and solvent.Greater the attraction, lower the solubility as more energy is required to separate the solvent molecules. The forces of attraction between the water molecules.Greater the attraction, lower the solubility as lattice energy is higher. The forces of attraction between the ions in the solid.Table: Changes in enthalpy and entropy of each stage of dissolution of ionic compounds. Chlorine ions are usually hydrated by more water molecules than sodium ions because of their larger ionic radius. Each ion is hydrated (surrounded) by exactly four water molecules. Hydration is an exothermic process.įigure: A simple drawing of the hydration process of dissociated Na + and Cl – ions. Intermolecular forces are formed between solutes and solvents, releasing energy in the process.


Each water molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds, causing it to have a relatively high boiling point for a molecule of its size.įigure: covalent bonds are intramolecular bonds which are much stronger than intermolecular hydrogen bonds between water molecules. Hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole forces and dispersion forces are present between water molecules. Separation of solvent molecules is endothermic as energy is absorbed to overcome intermolecular forces present between molecules.Dissolution of ionic compounds occurs in three steps:.For example, MgCl 2 has greater lattice energy than NaCl because magnesium ion has a +2 charge while sodium ion has a +1 charge. Greater the charge, higher the lattice energy. For example, KCl has lower lattice energy than NaCl because potassium ion is larger than sodium ion in terms of ionic radius.
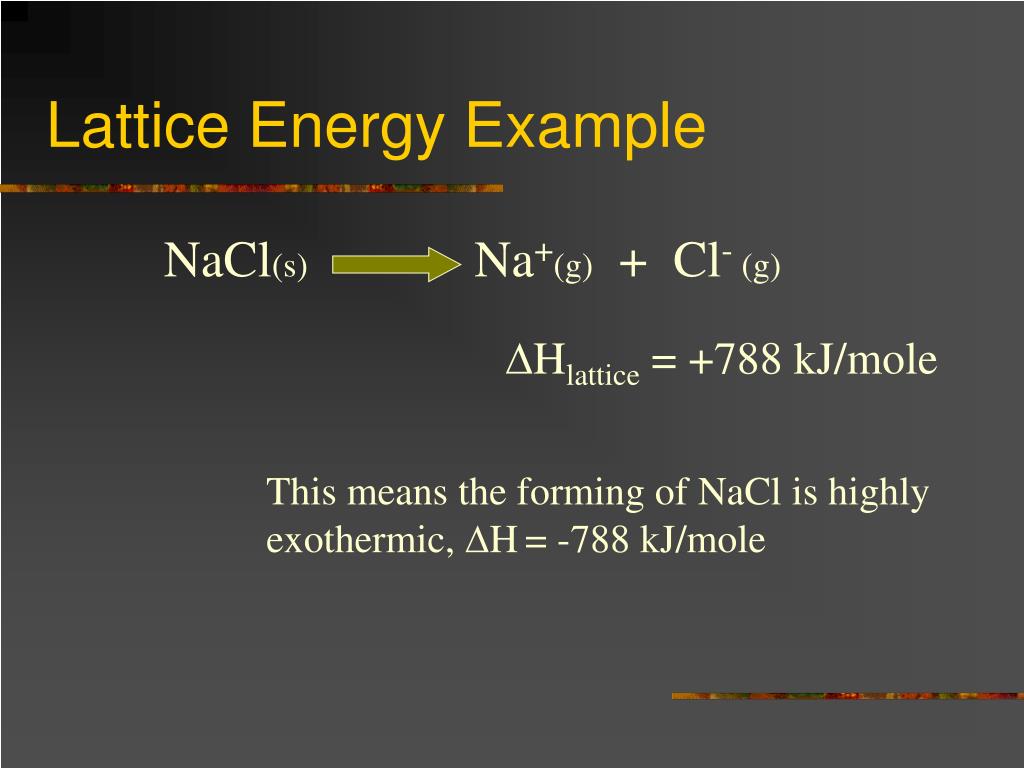
Larger the ions, lower the lattice energy. Lattice energy is dependent on two main factors:.$$$$įigure: Lattice energy of magnesium oxide is greater than that of sodium fluoride because magnesium and oxygen ions have greater charge. It is defined as the energy released through the formation of an ionic compound from its constituent ions.įor example, the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine ions releases 787 kilojoules of energy for every mole of sodium chloride. Lattice energy indicates bond strength of an ionic compound.Dissolution of ionic compounds requires energy equal to the lattice energy. Ionic compounds occupy a lattice structure, held together by electrostatic forces between cations and anions.This video will explore the different steps which are involved in the dissolution of an ionic compound - separation of water molecules, dissociation of compound into ions, hydration of ions. What are the processes involved in the dissolution of an ionic compound? This is part of the HSC Chemistry course under the topic equilibrium systems HSC Chemistry Syllabusĭescribe and analyse the processes involved in the dissolution of ionic compounds in water


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
